Self-Service Enablement
Standard API integration enabled automated customer self-service for quota increase requests.
This project demonstrates how cross-service knowledge sharing influenced the Service Quotas implementation for Amazon EVS. I recognized operational patterns from prior managed service launches and contributed those learnings during EVS public preview planning. This helped stakeholders adopt an automated solution that scales with customer demand while reducing friction and support overhead.
Previous managed service launches had prioritized rapid delivery using custom validation logic to check account quotas. While this met initial requirements, it often created downstream friction as adoption grew.
In those historical examples, customers needing quota increases often faced manual support workflows, creating wait times before they could proceed with deployment. As request volumes increased, these manual review cycles risked extending deployment timelines for customers ready to scale.
During EVS public preview planning, I identified that the service was trending toward a similar custom validation approach. This created an opportunity to apply those operational insights early, potentially avoiding the scaling challenges experienced by previous services.
During public preview planning, I shared these operational experiences with EVS product leadership. Rather than advocating for a specific technology, I focused on helping stakeholders understand the customer lifecycle implications.
Building Strategic Context:
I framed the decision as a balance between launch speed and Day 2 operability. While custom logic allows for faster initial release, deep integration with the standard Service Quotas API enables customer self-service. I presented data regarding request volume patterns and manual review overhead from similar services to illustrate the potential impact on the customer experience.
This context shifted the discussion from “launch deadlines” to “scalable customer experience.” EVS product leadership recognized that designing for self-service upfront would be more efficient than retrofitting the architecture post-launch.
I also advocated for reviewing quota defaults alongside the integration strategy. Restrictive initial quotas can create artificial barriers that force immediate support requests. I suggested calibrating defaults to accommodate typical “starter” use cases, eliminating unnecessary support tickets for standard onboarding.
Validation Through Public Preview:
Public preview deployment data confirmed the value of reducing friction. Early feedback highlighted that minimizing setup barriers was critical for successful first-time deployments.
The EVS product team adopted a multi-faceted approach informed by these cross-service insights. Beyond standard API integration, the team optimized quota defaults to better align with customer needs. Initial environment and host count limits were set to accommodate majority use cases without requiring immediate support intervention.
This strategic decision positioned EVS for better customer experience and operational efficiency.
Customer benefits:
Operational benefits:
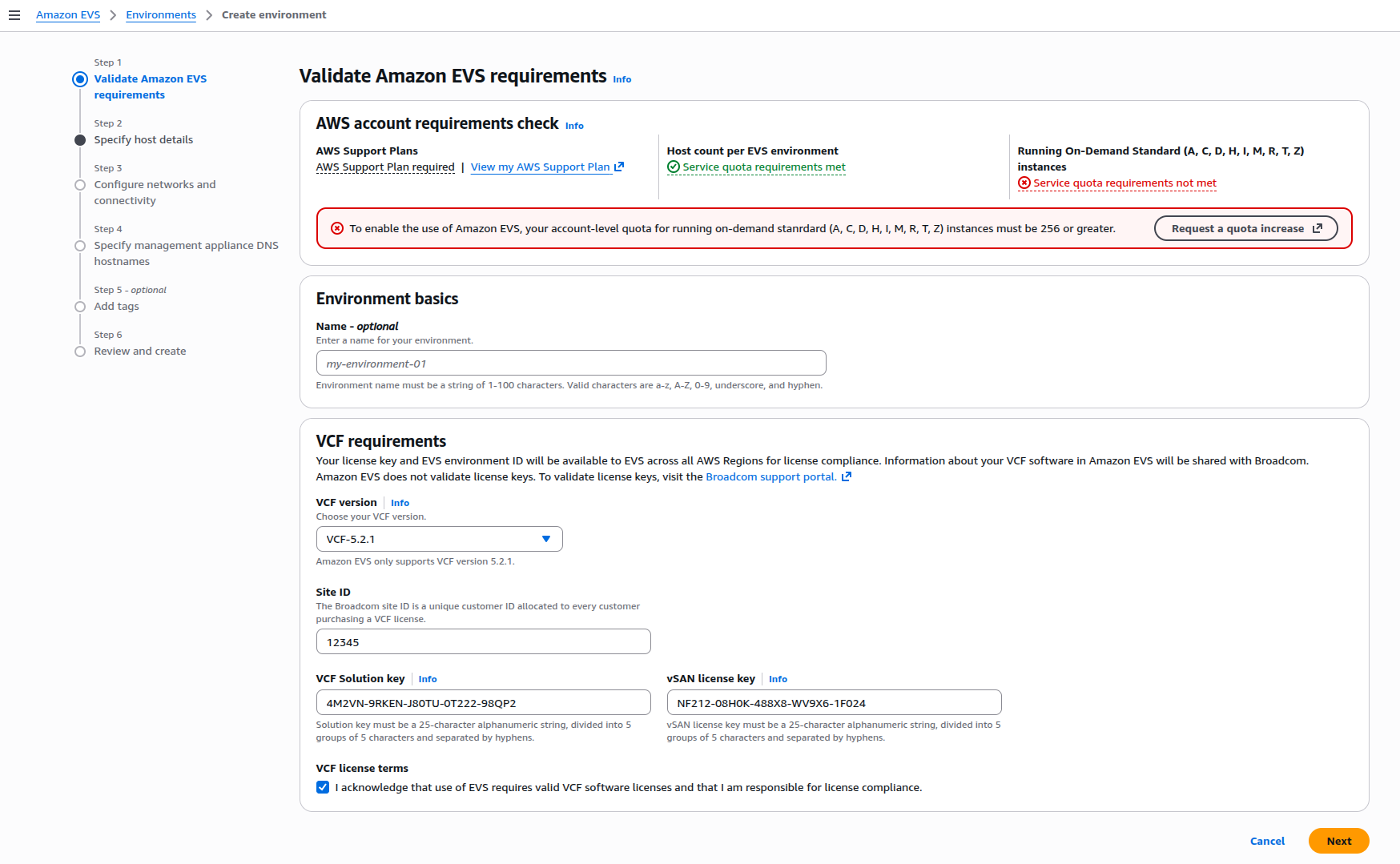 EVS Service Quotas validation in Create Environment wizard - validating On-Demand Standard instances quota requirements
EVS Service Quotas validation in Create Environment wizard - validating On-Demand Standard instances quota requirements
Self-Service Enablement
Standard API integration enabled automated customer self-service for quota increase requests.
Reduced Support Overhead
Significantly reduced the need for manual triage of standard quota increase requests.
Scalable Solution
AWS-standard integration approach scaled efficiently with customer adoption.
Proactive Validation
Automated quota checking provided early visibility into account readiness.
Operational experience with mature services creates valuable insights for new products. Recognizing implementation patterns and their downstream impacts enables proactive influence before architectural decisions are finalized.
Engaging product teams during the planning phase—before code is committed—creates an opportunity to shape direction with minimal disruption. Strategic decisions made early compound their value over time.
Abstract concerns about future scalability carry less weight than concrete historical data. Sharing specific insights about support case volume and manual triage overhead provided compelling evidence for investing in automation.